Adresse
304 Nord Kardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Arbeitszeiten
Montag bis Freitag: 7AM - 7PM
Am Wochenende: 10AM - 5PM
Adresse
304 Nord Kardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Arbeitszeiten
Montag bis Freitag: 7AM - 7PM
Am Wochenende: 10AM - 5PM
Electronics overheating causing failures? Standard cooling often bulky or inefficient. I know the challenge of finding reliable thermal management for sensitive components.
From my perspective as a manufacturer at ALUT, an excellent plate fin heat sink is the ultimate thermal solution for many applications due to its simple, robust design that efficiently transfers heat from a component to the air. We see its cost-effectiveness and reliability as key benefits.
This common cooling device plays a critical role in electronics reliability. Understanding the plate fin heat sink helps in selecting the best cooling method. Let’s explore what it is and how it achieves such efficient cooling.
Confused by thermal jargon? A “heat sink” sounds complex, but some designs, like the plate fin heat sink, are elegantly simple. I often explain these basics to clients looking for effective cooling.
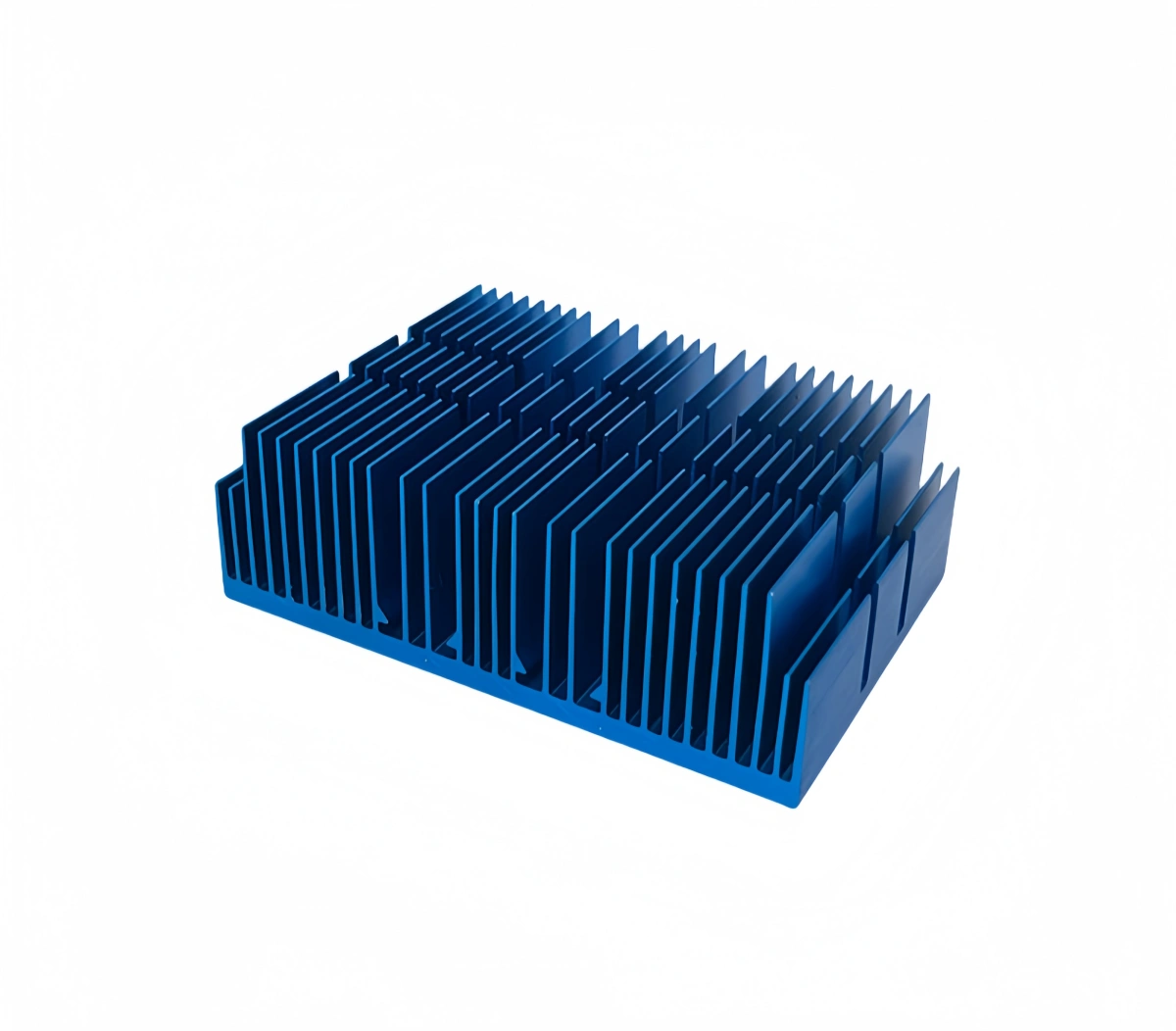
In my manufacturing work at ALUT, I define a plate fin heat sink as a passive thermal management component. It typically features a flat baseplate with multiple thin, parallel fins extending outwards, specifically designed to maximize surface area for heat dissipation into the surrounding air.
A plate fin heat sink is one of the most common and straightforward types of heat sinks used for thermal management in electronic devices and machinery. Its design is characterized by two primary components: a baseplate and a series of fins. This simple construction contributes to the wide adoption of the plate fin heat sink.
The fins in this type of heat sink are usually:
Heat just vanishes with these, right? Not quite. Understanding the science behind how a plate fin heat sink functions helps appreciate its clever design. I always find the physics fascinating.
From my viewpoint overseeing thermal component production at ALUT, a plate fin heat sink works through conduction and convection. Heat conducts from the hot device to the baseplate, then into the fins. The increased surface area of the fins then efficiently transfers this heat to the cooler ambient air via convection.
The operation of a plate fin heat sink relies on fundamental principles of heat transfer to move thermal energy away from a heat-generating source and dissipate it into the surrounding environment, typically air. The process involves two primary modes of heat transfer: conduction and convection.
The overall performance is often characterized by its thermal resistance (°C/W). A lower thermal resistance means a more effective cooling device.
Why choose this simple design when so many complex coolers exist? Sometimes, simple is best, and a plate fin heat sink offers many practical benefits. I’ve seen these reliable performers work effectively for decades in various applications.
In my experience at ALUT, a key plate fin heat sink advantage is its excellent balance of performance, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturing simplicity. We find these are often the most economical and reliable solution for a wide range of common thermal management needs.
This type of heat sink remains a popular choice for thermal management across numerous industries due to a compelling combination of advantages. While more complex solutions exist for extreme heat loads, the plate fin heat sink offers an optimal balance for many common applications.
This is often the most significant advantage.
A well-designed plate fin heat sink provides sufficient cooling for a vast range of electronic components. Its performance can be significantly enhanced with forced airflow.
Aluminum designs are lightweight, important where system weight is a concern, such as portable devices.
The plate fin heat sink is a well-understood and mature technology. Extensive research and design data are available, making it easier for engineers to predict performance.
| Advantage Category | Specific Benefit | Implication for Plate Fin Heat Sink Users |
| Cost | Simple manufacturing, affordable materials | Economical thermal solution for many budgets |
| Reliability | No moving parts, robust construction | Long lifespan, low failure rate, minimal maintenance |
| Performance | Good heat dissipation for moderate loads | Effective cooling for a wide range of electronics |
| Weight | Lightweight (especially aluminum) | Suitable for weight-sensitive applications |
| Flexibility | Scalable design, customizable parameters | Can be tailored to specific project needs |
| Maturity | Well-understood technology, ample design data | Predictable performance, easier design optimization |
Therefore, choosing a plate fin heat sink often means selecting a proven, economical, and reliable thermal solution.
So many heat sink types! Is the classic plate fin heat sink always the champion for cooling needs? Choosing the right one really depends on the specific thermal challenge your application faces.
From my perspective at ALUT, determining if a plate fin heat sink is ‘best’ depends on the application’s specific needs. For general-purpose cooling with moderate heat loads where cost is a key factor, I often find it superior. However, for very high heat densities or extreme space constraints, other types might be necessary.
The “best” heat sink is always the one that meets the thermal requirements reliably and cost-effectively. The plate fin heat sink is a strong contender in many scenarios, but it’s important to understand how it compares to other common types to make an informed decision. Considering a plate fin heat sink alongside alternatives is good engineering practice.
Here’s a look at how a typical aluminum design stacks up:
| Heat Sink Type | Typical Cost | Fin Density | Performance (Natural Conv.) | Performance (Forced Conv.) | Komplexität | Best For |
| Plate Fin (Extruded) | Low-Med | Med | Gut | Sehr gut | Niedrig | General purpose, moderate heat, cost-sensitive |
| Stamped | Sehr niedrig | Low-Med | Messe | Gut | Sehr niedrig | Low power, high volume, SMT components |
| Bonded Fin | Med-High | Hoch | Messe | Ausgezeichnet | Med-High | High power, forced air, large heat sinks |
| Skived Fin | Med-High | Sehr hoch | Gut | Ausgezeichnet | Med | High power, compact, good airflow |
| Folded Fin | Med | Hoch | Messe | Sehr gut | Med | Lightweight, ducted airflow |
| Liquid Cooling | Sehr hoch | N/A | N/A | Ultimate | Sehr hoch | Extreme heat loads, remote heat dissipation |
Ultimately, the choice involves balancing thermal performance, space, airflow, reliability, and budget. The plate fin heat sink provides a highly effective and economical solution for a broad spectrum of these scenarios.
Die plate fin heat sink offers excellent, reliable cooling for many needs. Its simple design ensures cost-effective thermal management, proving a powerful, essential component like the plate fin heat sink in electronics.